Biofilms are particularly challenging in the food industry due to their resistance to sanitizers, chemical cleaners, and antibiotics. Quorum sensing and EPS (extracellular polymeric substances) are shown to contribute to the formation and resistant qualities of biofilms.
What Are Biofilms?
In nature, most bacteria do not exist as suspended (planktonic free floating) cells. Bacteria live in a group (a mass of bacterial cells) attached to each other and to surfaces, in a biofilm form.
A biofilm is a complex community of microorganisms that are embedded in self-created extracellular polymeric substances (EPS).
A biofilm is a complex community of microorganisms that are embedded in self-created extracellular polymeric substances (EPS). Therefore, the biofilm is a microbial population adherent to each other and to surfaces or interfaces enclosed in the matrix. In a complex biofilm network of EPS, the bacterial cells perform less as individual cells and more as a collective living system, frequently creating channels to deliver nutrients and water to the cells inside the biofilm. To read the article in its entirety please click here.
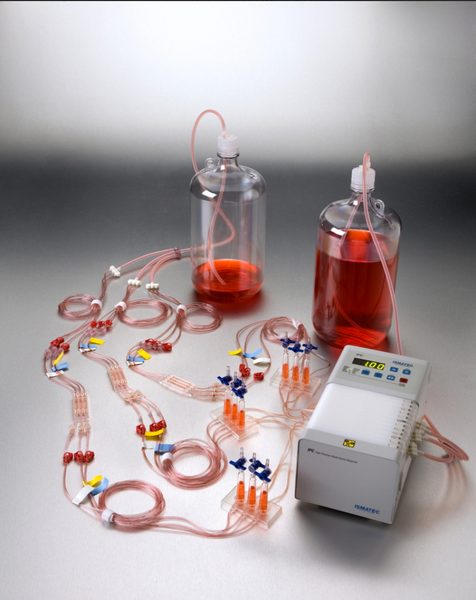
IBI Scientific manufactures 3-channel and convertible flow cells for the growth and real-time study of biofilms either with a standard light microscope or you can build a 3D image with the use of a confocal-laser microscope. IBI flow cell systems are designed to allow the introduction of other reagents/antibiotics and to gather the downstream effluent for expression studies.
For more information on IBI flow cells please click here.
(This information was taken from an article published by: Dr. Bassam Annous, Eastern Regional Research Center – USDA-ARS, NEA and Dr. Ruth Eden, Bioexpert. This article is the first in a series.)